Underlying concepts of Wikidata
Last updated on 2023-04-24 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 0 minutes
Overview
Questions
- What is a RDF triple?
- What are the underlying components of RDF?
Objectives
- Know what a triple is, and relate structure of a Wikidata statement to traditional metadata field structure
- Know how linked data can create more context for patrons/users in library catalogs
- Know how linked data can improve recall in library catalogs? (TODO: Check if we want to address this here).
2.1 Concepts foundations: ways of storing data.
There are many types of databases, the most common types are:
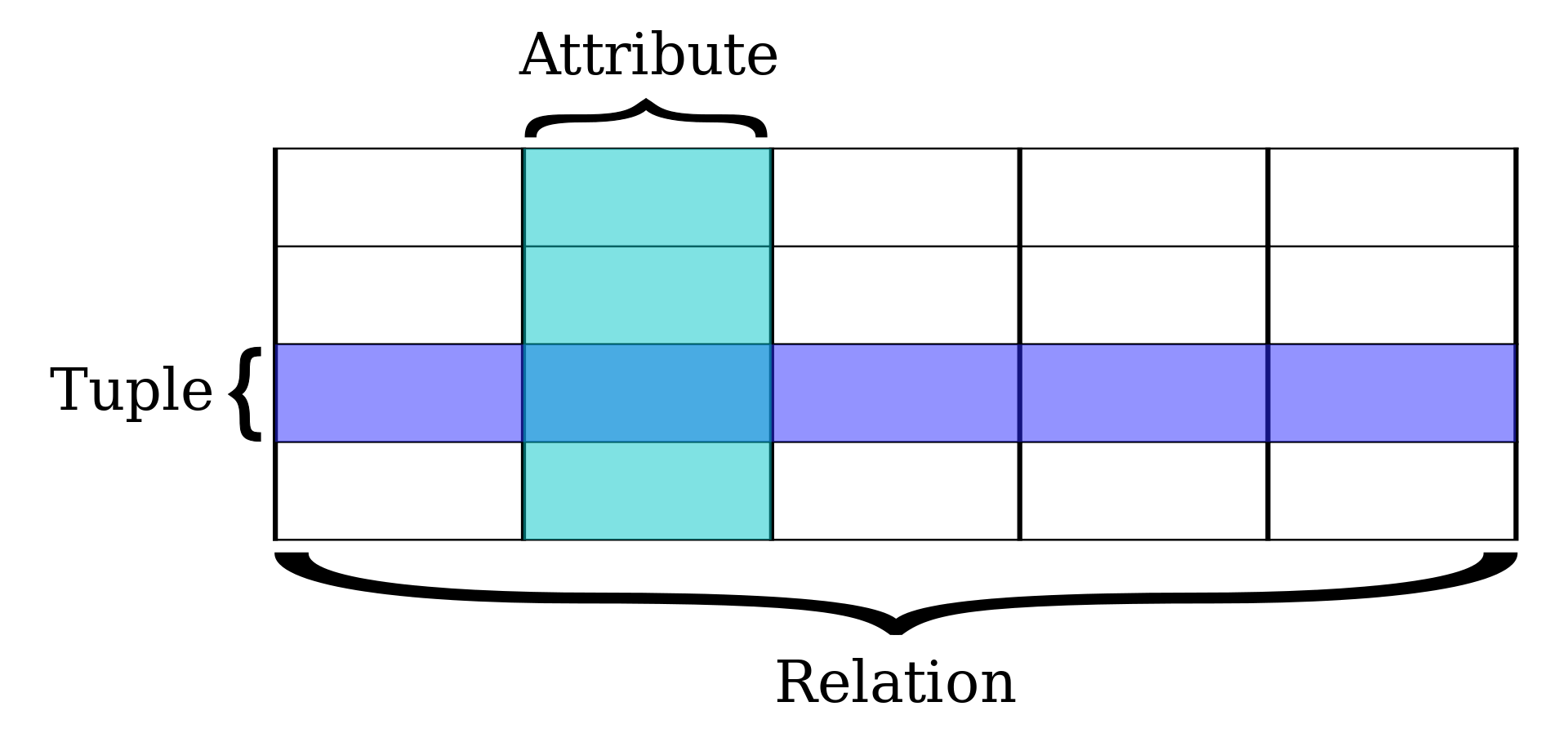
2.1.1 Relational databases:
A relational database is a set of formally described related tables
from which data can be accessed or reassembled. This model organizes
data into one or more tables (or “relations”) of columns and rows, with
a unique key identifying each row. each table/relation represents one
“entity type” and these entities are connected via constrained
relationships. This model is fully structured and mostly uses SQL
(Structured Query Language) to retrive and manuplate data.
Examples:
2.1.2 Graph / Semantic databases
Semantic web is an extension of the World Wide Web standards, which promote common data formats and exchange protocols on the Web, most fundamentally the Resource Description Framework (RDF) is used to store data. Most RDF fundamentally uses SPARQL (Simple Protocol and Rdf Query Language) to read stored data while relational databases uses SQL (Structured Query Language) to do so. In SQL relational database terms, RDF data can also be considered or viewed as a table with only three columns – the subject column, the predicate column, and the object column.
2.2 Concepts foundations (RDF and RDF triples)
The RDF is a conceptual data model, It is based on the idea of making statements about resources in expressions of the form (subject–predicate–object), known as triples.
The subject denotes the resource, and the predicate denotes traits or aspects of the resource, and expresses a relationship between the subject and the object, for example: John-is-a person, John-born in-1980, John-works as-Engineer
RDF data are stored on containers known as triplestores.

2.3 Underlying components
- Items
Items represents subjects such Douglas Adams and have identifiers that starts with letter “Q” like: Q42 for Douglas Adams.
Each item must have a name in one or more langauges, optionally have alternative names and descrition. - Properties
Properties represents attributes of the subject such occupation and have identifiers that starts with letter “P” like: P106 for Occupation. - Claims
Claims are the triples, which combine the formation of Item and Property and a value such: Douglas Adams (Q42) - occupation (P106) - comedian.
Note: value can be already stored in wikidata, therefore the bot assigns the Q number of the value instead. - Statement
A Claim is a part of a statement, a statement also includes: References, Ranks, and Qualifiers. - References
Used to store the source of the claim, using properties, such stated in, qoute, and etc. - Ranks
A useful component to mark outdated claims. - Qualifiers
Qualifiers are besicly properties but on claims rather than items.
Is data stored in the RDF triple format part of your work as a librarian?
Take some time to think about if data stored in the RDF triple format is part of your work as a librarian. Can you give an example in the format of an RDF triplet?
TO DO: PLEASE ADD A REAL LIFE EXAMPLE
Point out one RDF triple on the Wikidata item page of former astronaut Mae Jemison.
Got to the Wikidata page of Mae Jemison and point out one RDF triple. An RDF triplet consists of a subject, a predicate and an object. Can you assign the three corresponding Wikidata terms?
Got to Wikidata and either search for “Mae Jemison” or enter the ID
Q34091. In the picture below the statement “Mae C. Jemison -
part of - NASA Astronaut Group 12” is an RDF triple. 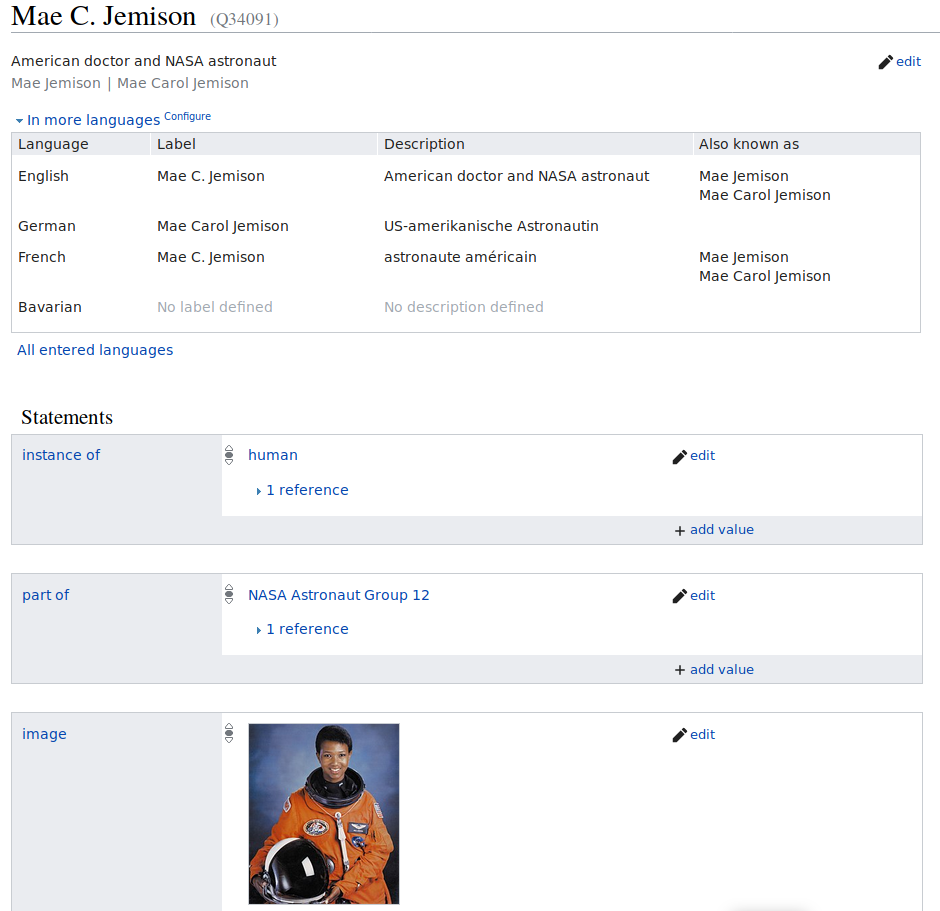
Screenshot of Wikidata Main
Page
2.4 Scholia - a webserive with Wikidata as underlying database
- Introduction with The Linked Open Data Cloud
- the structure enables queries
- reference to DBPedia
- you can build your own web services with Wikidata as database >
Scholia
- e.g. search for Alex Bateman
2.5 Wikidata one pager
2.6 How Wikidata compares with other data sets
FIXME
- First key point. (FIXME)
